One of the hardest things about route optimization is this:
How do you know if your routes are actually efficient?
It’s a tough question to answer. Especially because it can take months for results and returns to really kick in.
Well, today you’re going to see exactly what route data you need to use to optimize routes. How to track them. And how to double down on what’s already driving the best results in the market: data-driven route optimization.
With that, here’s what you need to know about routing data.
And the top 10 most important route data to collect and monitor in 2024.
What Is Route Data?
Route data are specific factors used to determine the most efficient route for a given set of constraints or objectives. Route data enables you to plan routes based on location data, geolocation data, vehicle weight, depot and driver service schedules, and route information.
In short:
Routing data is the information you need to use to plan a route and evaluate its efficiency.
(Basically a way to optimize routes that’s accurate and guaranteed to be effective.)

Types of Routing Data Used in Route Planning
Different types of route data enables you to take a data-driven approach to route planning. It’s also what allows you to select the best route based on task requirements, available resources, and the cost-effectiveness of the route.
Here are the most common types of data that helps you to do just that:
- Location data: Location information is essential for knowing where drivers have to go (and how to plan better delivery routes). It includes customer addresses, pick-up and drop-off locations, stores, depots, warehouses, and storage facilities, as well as petrol stations and vehicle repair shops.
- Geospatial data: Geographical information helps you to accurately find the shortest and quickest routes. It includes information about road networks, start points and endpoints, route waypoints, distance between stops, and geocoding data that precisely maps out the location of each stop based on longitude and latitude.
- Time windows: Taking into account different pickup or drop-off time windows is crucial for route planning. This includes pickup-by and deliver-by dates and times. Delivery windows tell you when customers expect to receive orders (customer availability and business hours), which helps you to plan and order stops to ensure on-time delivery.
- Service time windows: Considering how long it takes to complete a delivery drop off or a service call has affects the number of stops you can plan on a route. This includes the time drivers have to perform customer tasks: handing off packages and goods, servicing customers, collecting proof of delivery, or waiting on customers to receive the order.
- Driver data: Route optimization takes into account a variety of driver data. This helps you to comply with regulations that safeguard drivers’ well-being and protect the company. It includes driver availability, work hours, break times, holidays, skills or certifications, tools and equipment, customer preferences, and delivery performance.
- Vehicle data: Vehicle data is vital when managing both internal fleets and last-mile carriers. This data includes vehicle model, size, capabilities, fuel consumption and efficiency, speed limits, payload capacity, and on-board equipment. Based on this information routing software helps you with load balancing and resource allocation.
- Traffic data: Collecting traffic information helps you to optimize routes and avoid delays. This includes historical, real-time, and predictive data on traffic flow, traffic congestion, road works, road closures, and accidents.
- Road network data: Data about road networks helps you to select the best types of roads for your routes and vehicles. This includes information about speed limits, traffic lights, left-hand turns, stops, one-way vs. two-way streets, tolls, highways and exits, bridges, tunnels, weight or height limits for vehicles, and other factors.
- Weather data: Weather can affect your decision to choose a route. Having access to a weather forecast can help you to prevent delays, plan detours and alternative routes, and prepare drivers and vehicles for bad weather. This ensures the safety of your drivers and cargo. And in cases of severe weather, it helps you to cancel orders to prevent loss.
- Historical route data: Analyzing historical route data improves how you plan and optimize future routes. It reveals areas of operations that you need to upgrade and allows you to pinpoint opportunities for continuous optimization. This can include route times, fuel consumption, stop density, and other key performance indicators.
- Customer preference data: Collecting customer data about their service preferences is a way of planning routes that provides the best delivery experience. Taking into account preferred packaging, drop off points, drivers, time of delivery, and type of communication is what makes your customers happier and more loyal.
- Load data: When you operate out of several pickup locations, information about how, when, and where products are loaded onto vehicles has an impact on route optimization. Load data allows you to account for picking and packing orders, load sequencing at depot sites, loading times, and load balancing when planning routes.
- Order priority data: Some deliveries have a priority over others. This information affects the stop order on a route and when need to fast track delivery. Especially with time-sensitive deliveries, such as overnight shipping, next-day or same-day deliveries.
- Cost data: The best routes are usually the most cost-effective ones. That’s why it is necessary to consider operational and transportation costs when planning a route. Fuel cost, employee payroll, facility and vehicle maintenance costs, outsourcing, tolls, and other operating costs can account for 50.3% of your logistical spending.
- Vehicle availability data: The amount of orders you can deliver depends on the number of vehicles you have available. This means that you need to take into account any scheduled vehicle maintenance or repair appointments when planning your routes. That will give you an accurate assessment of the total payload capacity of your fleet.
- Historical performance data: Analyzing historical performance data reveals your delivery performance over time. Information about delivery success rates, lateness, number of failed delivery attempts, and customer feedback can help you to identify areas of operations that you need to improve and optimize.
- Real-time tracking data: On-board telematics and GPS devices, as well as advanced route optimization software allows you to track driver location and performance in real time. This can help you make route adjustments, plan returns on the go, and use dynamic route optimization to stay flexible even when something doesn’t go to plan.
- Predictive analytics data: Predictive analytics combines historical route data, machine learning, and statistical models to forecast situations that may affect the efficiency of your routes. Using predictive analytics data when planning routes helps you to allocate resources intelligently and prepare for route adjustments before you need to make them.
Challenges of Collecting and Implementing Route Data
Using data to plan routes is extremely advantageous. In fact, we recently published a case study about Crocus that showcases this:

Still, it’s a strategic decision that does come with significant challenges to your organization. (just like any other tech investment):
- Data accuracy and availability: Route optimization relies on the quality of your data. If the data is inaccurate, out-of-date, or insufficient, you’ll essentially end up with ineffective routes (and a whole lot of wasted time planning such routes). Collecting and maintaining data that’s accurate, up-to-date, and available at a moment’s notice is difficult.
- Integration with current systems: Route planning integration with existing systems is a common problem we see businesses face when starting to use routing data. This includes enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM), order and inventory management systems. Integration is necessary to allow the easy access and flow of data between all of these systems, which ensures the data itself is always accurate and up-to-date across your entire operation.
- Real-time data processing: The amount of data that’s required to effectively plan and optimize routes is enormous. That’s why it is necessary to deploy IoT devices and a robust IT infrastructure centered around a cutting-edge route optimization system. This allows you to handle huge volumes of data uninterruptedly in real time.
- Implementation costs: Setting up an intelligent route optimization system is quite the investment. This includes the cost of the software itself, necessary hardware upgrades, continuous maintenance, plus the cost of training employees to collect and use route data when performing day-to-day tasks.
- Internet connectivity: Collecting live routing data and updating that information in real time is a challenge in areas with poor internet connectivity. This can affect how you receive and share data to and from the road, and what data you can access.
- Data security and privacy: Inadequate data protection and security, especially when handling large volumes of confidential and sensitive data relating to customers can be a big issue. That’s why the systems that collect and process the data have to be secure.
How Can eLogii Help You to Drive Efficiency Using Route Data?
eLogii is an intelligent route optimization software that relies on route data to simplify and streamline how you plan and optimize routes. In fact, we have already helped hundreds of businesses leverage route data to optimize their operations, with new case studies being published every week.
To determine the most efficient and cost-effective routes, eLogii takes into account a variety of routing data. The software also helps you to collect, process, and analyze all route information in real time, which streamlines the flow of data across your operations.
While all of the information is stored and easily accessible on the cloud. Which makes it secure. And you can easily use the data to evaluate performance with route analytics for better decision making and continuous optimization.
Here are the key features of eLogii that make it easier to collect, analyze, and leverage route data when managing your delivery or field service:
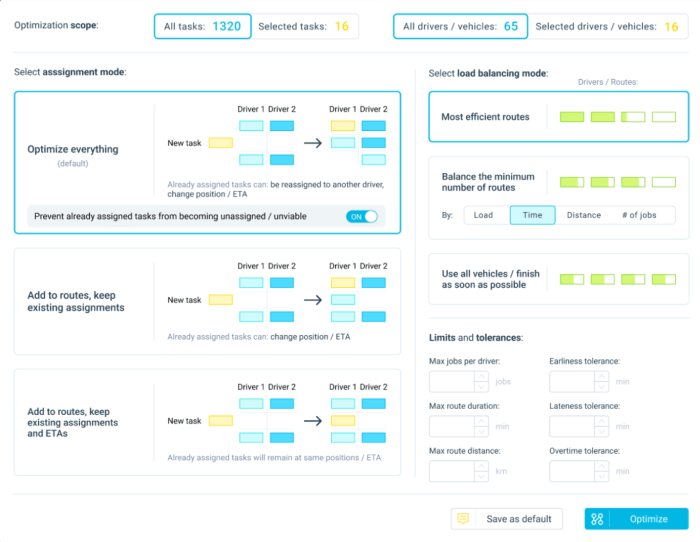
- Constraints-based route optimization: eLogii enables you to add time and delivery constraints with our route optimization modes. You can enter delivery windows, order priority, balance vehicle loads, and determine how the software assigns tasks to drivers.
- Live driver tracking: Driver tracking is one of eLogii’s main software features that lets you to keep track of driver locations in real time. It also gives you complete visibility over operations, and collects related to driver performance and any unexpected delays.

- Data analytics and reporting: We’ve already mentioned in depth how and what kind of data and analytics eLogii can capture and display, both historically and in real-time. But you can also export this information as reports for customers and stakeholders.

- Delivery status reports: eLogii allows you to set up notification links and automated text or email messages that you can share with customers. These reports give insight into the status of each delivery, with progress, status, and estimated time of arrival.

- Proof of delivery: Drivers can collect proof of delivery using the driver app on their mobile devices. You can use this feature to collect customer information, which can help you to customize your service based on the individual needs of your customers.

- Integration: eLogii’s powerful route optimization API allows you to connect with any other business software you use to manage your operations. This smooth cross-platform data sharing helps you to boost efficiency across other aspects of your business.

And there’s a lot more features and capabilities that you can still uncover.
So…
